Synthetic Nodes
Version: 1.0.0
Pattern language family: BN
Modeling phase:
2. The conceptualization phase of a system of interest
3. The technical implementation
Modeling step:
5. Choice of how model structure and parameter values are to be determined
7. Identification of model structure and parameters' values
Problem:
How to model a variable which value is determined by the values of some other variables, however the relationship between them is not causal?
Solution:
In this case the variable can be "synthesized" from its determining variables through a combination rule. The synthesized variable will be the child of all the determining variables. The value, or the conditional probability, of the synthesized variable will be either deterministic, or converted into stochastic by adding a probabilistic noise term to the combination rule.
Applying this pattern enable the user to represent relationships that are not fully causal in the network, as well as enabling the user to embed hierarchical structures into the network.
Structure: The solution proposed by this pattern have the following structure in a BN:
-
Assume that the variable $S$ can be driven from the variables $A, B, C$ through a certain combination rule, so that $S=f(A,B,C)$.
-
The value of the synthetic node can be determined by one of three cases:
-
The combination rule is fully known, i.e. deterministic function, and the value of $S$ can be deterministically derived from its parents. In this case, $S$ is a deterministic variable.
-
The relationship between $S$ and its parents is not fully deterministic, so the value of $S$ can be derived from its parents plus a noise term represented using a suitable probability distribution, i.e.
\[S = f(A,B,C) + P(\theta)\] -
The relationship between $S$ and its parents is not known. In such case, a principle component model can be used to link $S$ to its parents (refer to the pattern "Latent States" for more details)
-
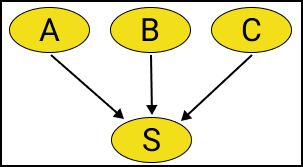
Fig.1 The variable S is synthesized from other variables which it has no causal relation with them.
Constraints:
This solution works under the following conditions:
- In the absence of the causal relation between the synthetic node and its parents, there should a logical connection between child node and the parent nodes.
Related patterns:
Design choice and model quality:
- 2.R
- 4.R
Resources:
- Neil, M., Fenton, N., & Nielson, L. (2000). Building large-scale Bayesian networks. The Knowledge Engineering Review, 15(3), 257-284.