Local dependence confirmation
Version: 1.0.0
Pattern language family: BN
Modeling phase:
2. The conceptualization phase of a system of interest
Modeling step:
3. Conceptualization of the system, specification of data and other prior knowledge
5. Choice of how model structure and parameter values are to be determined
Problem: One of the fundamental assumptions underlying BNs is local dependence, i.e. the parents of a single node or the child nodes of a parent node should be independent and uncorrelated.
Solution:
This problem is solved by testing local structures for correlation before running network inference. If correlation between variables are found to exceed a certain threshold, e.g. Pearson correlation coefficient $(r)$ of $0.7$, this can be solved by either:
-
Linking the correlated variables by an edge which direction represent a cause-effect relation between the correlated variables.
-
Excluding the variables that have the least causal effect.
Structure: The solution proposed by this pattern have the following structure in a BN:
-
In the shown networks in Fig.1, correlation between $X_1$ and $X_2$ is $>r$.
-
In A and C, $X_1$ and $X_2$ are linked.
-
In B and D, $X_2$ is excluded from the network.
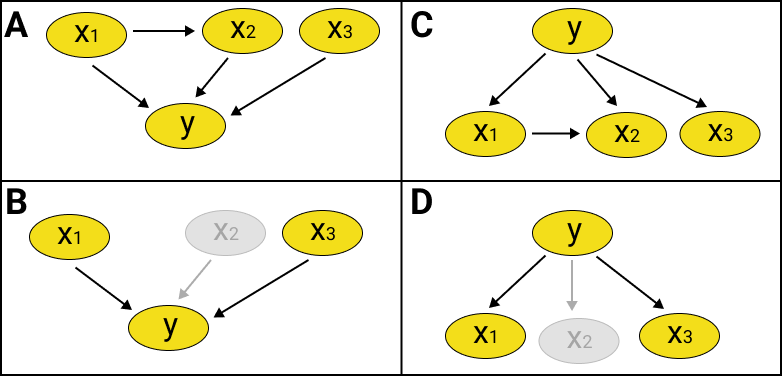
Fig.1 Changes in BN structure to adapt the correlation between variables.
Constraints:
The constraints for this solution are as follows:
- If the solution of variable exclusion from the network is to be applied, it is important to confirm that the excluded variable is not important to the causal interpretation of other variables.
Related patterns:
Design choice and model quality:
- 2.U
Resources:
-
Almond, R. G., Mulder, J., Hemat, L. A., & Yan, D. (2009). Bayesian network models for local dependence among observable outcome variables. Journal of Educational and Behavioral Statistics, 34(4), 491-521.
-
Marcot, B. G. (2017). Common quandaries and their practical solutions in Bayesian network modeling. Ecological Modelling, 358, 1-9.